The adoption of smartphones, smart devices, and IoT (Internet of Things) has made online security more important than ever. Modern hackers are highly skilled professionals who use sophisticated techniques to compromise your data and steal your identity. With the increased sophistication in hacking methods, it is not enough that you have strong passwords or a robust firewall on all of your systems. Thankfully, now we have 2FA and MFA to ensure tighter security on your accounts.
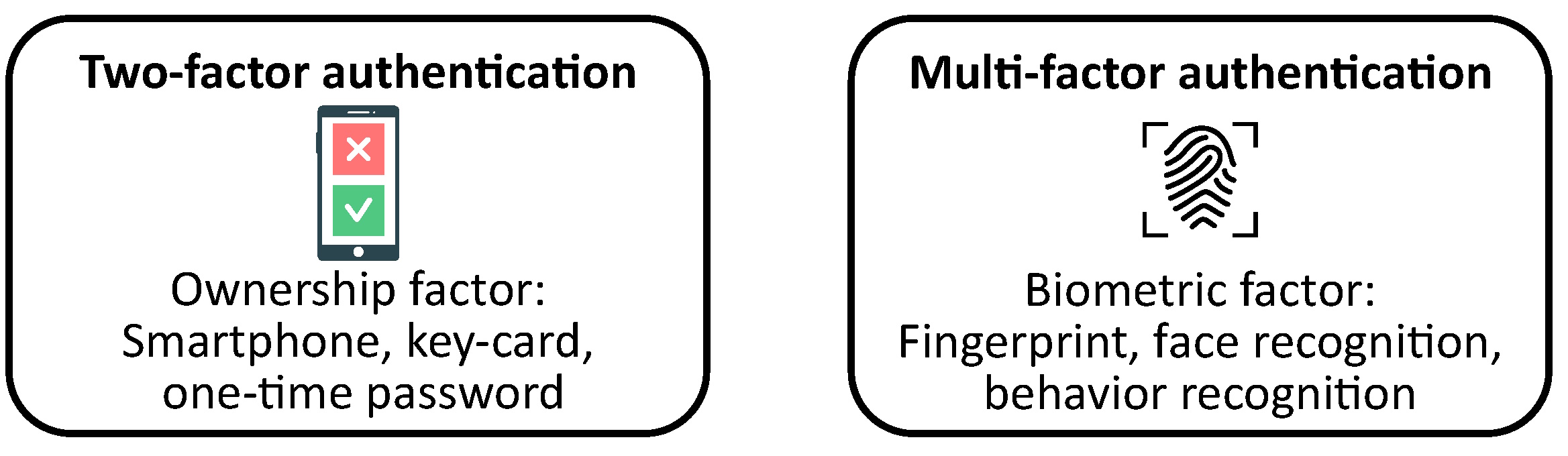
Short summary: What do 2FA and MFA mean? 2FA (“two-factor authentication”) is a way of adding extra security to your online accounts by asking for two different types of information to prove that you are who you say you are. MFA (“multi-factor authentication.”) is like 2FA, but instead of just two factors, you need to provide three or more different types of information to prove your identity.
2FA and MFA are important because they help keep your accounts safe from hackers or other people who might try to steal your information. By adding an extra layer of security, it’s much harder for someone to access your accounts without your permission.
In this article, we’ll explore the differences between Two-Factor and Multi-Factor authentication, and how they help add better security to your online data.
It appears that coming up with a password for our online channels isn’t enough.
This is unlike what we experienced five years ago, and this new development is a bit of a struggle for all of us.
I used to have a long list of passwords for my online channels, and I’d often change them to make sure no one can access my account information and credentials.
It helped a lot with keeping my user accounts and app safe. But today, having a long list of passwords and changing them often isn’t enough.
With the advent of technology and innovation, our password alone isn’t enough for security to keep our account and app credentials and information secure.
More and more end-users are exploring different options to secure and reinforce their online channels, such as the two-factor authentication solution (2FA) and multi-factor authentication solution (MFA).
I’ve added this extra layer of protection to make sure no one can access my accounts and app. And honestly, the different authentication factors are solutions I should have applied earlier.
It’s a full-proof way for end-users to avoid online scammers and phishers from accessing my data.
MFA: Multi-Factor Authentication Security
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security measure that requires multiple authentication factors to verify the user’s identity.
Authentication factors include something the user knows, such as a username and password, something the user has, such as a hardware token, and something the user is, such as voice recognition.
MFA adds an extra layer of security to user accounts, as it requires at least two or more authentication factors to be provided before access is granted.
Some common authentication factors include possession factor, such as a hardware token, and knowledge factor, such as a username and password.
Additionally, MFA may also include biometric authentication factors, such as voice recognition, and security questions.
SMS codes can also be used as an authentication factor, where the user is required to enter a one-time code sent to their mobile device.
Overall, MFA helps to prevent unauthorized access to user accounts and provides an added layer of security against security threats.
For today’s discussion, we will be talking about how end users can reinforce their online channels. Let’s start with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a new way of providing end-users with security and control over their channels. Inputting your username and password alone isn’t enough.
Instead, through MFA, a user now has to provide additional information to prove their identity.
This is one of the best authentication methods out there, considering how no one (who doesn’t know the user well) can access their account.
If you aren’t the real account user, you’ll have a hard time proving the identity of the account owner.
Using Facebook as an Example
Let’s use a classic illustration of MFA with logging in to my Facebook account. It’s something we can all relate to.
Step 1: Log in to Your Account
The first step isn’t anything new to us all. We’ve been doing it for years, even way before any sort of authentication system.
Simply input your username and password, and hit the enter button. This step is essentially the same for all social media channels.
Step 2: Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Security Keys
Before, once I hit the enter button, I’m directed to the homepage of my Facebook account. But things are a lot different with how I use my Facebook.
With a multi-factor authentication (MFA) system in place, I am asked to verify my identity through authentication factors. This is usually done through my username & password along with either of the following:
- Two-factor authentication;
- Security Keys
- SMS confirmation code; or
- Allowing/confirming the sign-in on another saved browser.
This step is the crucial part because if you don’t have access to any of those, you won’t be able to access your account. Well, at least not if you reset your password.
Now, take note: A lot of users DON’T have MFA set up just yet. Some stick with the traditional way of signing in, which makes them highly susceptible to hacking and phishing.
A user can manually enable all their social channels to have an authentication system in place if theirs doesn’t have one yet.
Step 3: Verify Your User Account
And once you’ve proven your identity, you’re immediately directed to your user account. Easy right?
It may take some extra steps to get multi-factor authentication (MFA) enabled. But for the added security and protection, I think it’s worth it for every user.
The Importance of Online Security for the User: Why Users Need Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)
As if it weren’t obvious enough, multi-factor authentication (MFA) is crucial for security reasons, regardless of the user!
In the real world, we all have the right to be secured in our persons, houses, and more. After all, we don’t want any unnecessary intrusions in our life.
MFA Protects Your Online Presence
Consider your online presence to be the same. Surely, users don’t want anyone stealing and intruding on any information they share in the online world.
And this isn’t just any kind of information, because today, many users even share confidential data about themselves like:
- Bank card
- Home address
- Email address
- Contact number
- Information credentials
- Bank cards
MFA Protects You From Online Shopping Hacks!
Unknowingly, every user has shared all that information one way or another. Like that time when you bought something online!
You had to input your card information, address, and more. Now just imagine if someone has access to all that data. They can use the data for themselves. Yikes!
This is why having multi-factor authentication (MFA) is important! And as a user, you don’t want to learn this lesson the hard way.
MFA Makes It Harder for Hackers to Steal Your Data
You don’t want to wait until all your data has been stolen before you reinforce your account/s.
MFA is an important system for all users. Heck, all sorts of authentication factors are vital for the user.
Whether you’re an individual user trying to secure your online data or an entity that has access to the personal information of users, MFA secures your thoughts and relieves your anxiety of possible confidential information leaks.
An entity having a reinforced factor authentication system is a big plus.
Users and customers will feel more at ease and have more confidence over a company that has a reinforced (MFA) multi-factor authentication security system in place.
Different (MFA) Multi-Factor Authentication Solutions to Protect Your Account
A web browser is an essential tool for accessing and interacting with web-based applications and services.
It provides a user interface for browsing and interacting with web content, and it’s crucial to keep it up-to-date to ensure security and stability.
Outdated web browsers can be vulnerable to security threats, such as malware, phishing, and other types of cyberattacks, which can compromise user data and system integrity.
Therefore, it’s important to regularly update your web browser to the latest version and ensure that it’s configured with appropriate security settings.
Additionally, users should be cautious when browsing the web and avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown files to reduce the risk of security breaches.
Overall, maintaining a secure and up-to-date web browser is critical for protecting user data and ensuring a safe browsing experience.
There are different MFA solutions to protect your account. Thanks to technology and innovation, you’ve got a ton of choices to choose from.
I’ll discuss some of the most common MFA solutions today to give you a brief idea of how they work.
Inherence
Inherence makes use of a specific physical trait/characteristic of a person. For example, this could be my fingerprint, voice or facial recognition, or retina scan.
One of the most common MFA a user uses today is through a fingerprint scan. It’s so common that the majority of mobile devices already have fingerprint scans or facial recognition setup in place!
No one else will be able to access your user account but yourself. For cases like ATM withdrawals, for instance, inherence is one of the best authentication factors.
Knowledge Factor
Knowledge authentication methods make use of the personal information or answers to questions the user gave.
What makes this a great multi-factor authentication factor is you can be as specific and creative with the passwords you make.
Personally, I make sure my passwords don’t just consist of the usual birthday digits combination. Instead, make it a combination of big and small letters, symbols, and punctuations.
Make your password as hard as possible. The likelihood of anyone guessing it is close to 0.
Besides your password, knowledge can also take the form of asking questions. You can set the questions yourself, and ask things like:
- What brand of shirt was I wearing when creating my password?
- What’s the eye color of my pet guinea pig?
- What type of pasta do I enjoy?
You can be as creative as you want with the questions. Just make sure to remember the answers of course!
I’ve had this problem before where I’d come up with weird questions, only to forget the answers I saved. And of course, I ended up unable to access my user account.
Location-Based
Another great form of factor authentication is location-based. It looks at your geographic location, address, among others.
I hate to break it to you, but many of your online channels probably have and collect information about your location. This is especially true if you have location enabled on your devices, all the time.
You see, with your location on, online platforms can develop a pattern of who you are. But if you use a VPN, keeping your location accurate may be a challenge.
Just the other day, I tried signing in to my Facebook account using a different device and in a different town.
Even before I was able to log in, I received a notification on my mobile device, telling me that there was an authentication attempt from someone from that specific place.
Of course, I enabled the transaction since it was me trying to access my account. But if it wasn’t me, at least I know that there was someone from that place trying to access and steal my identity.
Possession Factor
Another great factor authentication to confirm your identity is through the possession factor. For credit card users, the best example of possession I can give is OTP.
Possession takes place in the form of a one-time password (OTP), security key, pin, among others.
For example, each time I log in to my Facebook on a new device, an OTP or pin is sent to my mobile device. My browser would then direct me to a page where I need to input the OTP or pin before I’m able to log in.
It’s a clever way of confirming your identity, and a reliable authentication factor worth using since the OTP is ONLY sent to the registered mobile number.
To Sum It All Up About Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
There are various multi-factor authentication/MFA to explore out there, and I’m sure you’ll find something that’s more convenient and accessible for you.
With various MFA solutions available, I highly recommend using MFA for sensitive data like your bank account, credit card purchases, and sensitive website logins like PayPal, Transferwise, Payoneer, etc.
Furthermore, it’s easy to set up MFA on your mobile device.
For example, most banking websites have a section where you can add MFA as part of your security. You can also go to your bank and request for MFA on your account.
2FA: Two-Factor Authentication Security
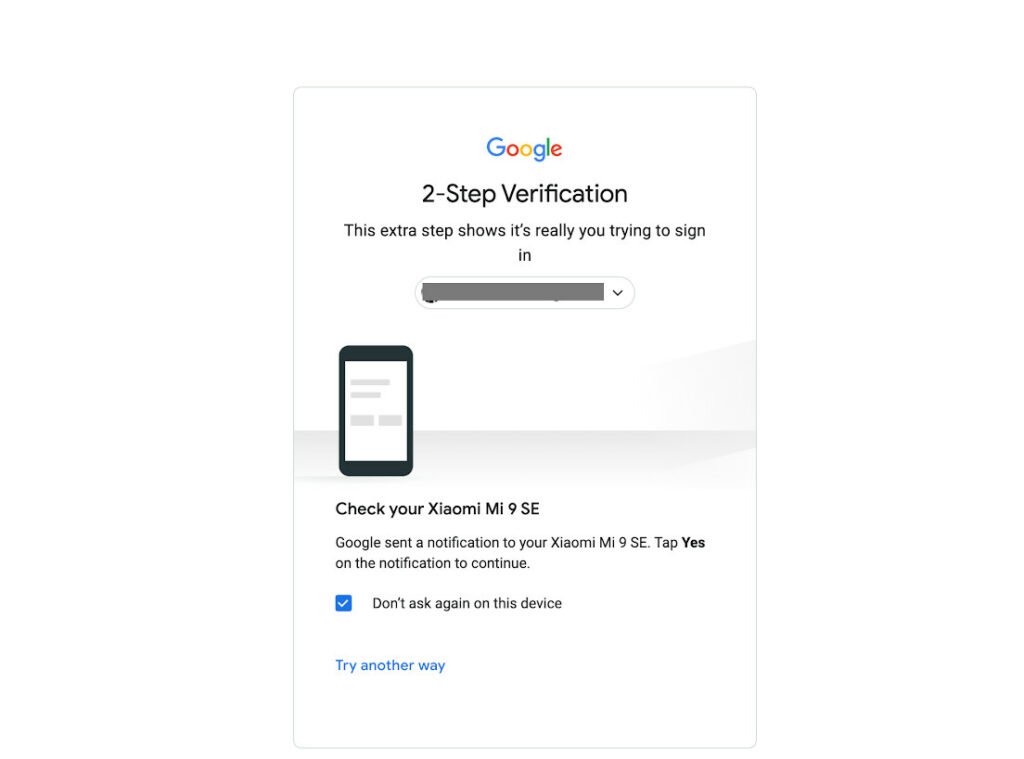
Now onto our next discussion: Two Factor Authentication (2FA). Two-factor authentication/2FA and multi-factor authentication/MFA aren’t far from each other.
In fact, 2FA is a type of MFA!
Two-factor authentication has made significant strides in terms of reinforcing our online data. Whether it’s a personal account or a big organization, 2FA does the job well.
I feel more secure knowing that I have an extra layer of protection and authentication plan for my online channels.
How 2FA Authentication Plays a Vital Role in User Authentication
Despite the presence of many incidents of cyber hacking and phishing, there are still several users who are convinced that 2FA and MFA are not necessary.
Unfortunately, with cyberhacking becoming increasingly rampant, obtaining one’s personal information is hardly a challenge these days.
And I’m sure you’re no stranger to cyber hacking yourself. You, or someone you know, might have already been a victim of these untoward incidents. Yikes!
The beauty of 2FA is there’s an external mechanism for you to confirm your identity. Some examples of 2FA include:
- OTP sent through mobile number or email
- Push notification
- Identity verification system; fingerprint scan
- Authenticator app
Is this important? Why, yes of course! Instead of being able to access your information in the first instance, there’s another form of authentication that a potential hacker has to go through.
It’s challenging for hackers to get hold of your account for sure.
Risks & Threats That Two Factor Authentication Eliminates
I can’t emphasize enough how 2FA can make significant strides in protecting your account.
Whether you’re a small organization, an individual, or from the government, having an extra layer of security is vital.
If you aren’t convinced that 2FA is necessary, allow me to convince you.
I’ve identified some of the common risks and threats users face that two-factor authentication can eliminate.
Brute-Force Attack
Even without the hacker knowing what your password is they can make a guess. A brute force attack is anything but simple, making a multitude of attempts to guess your passwords.
A brute force attack generates an infinite number of trials and errors to guess your password. And make no mistake thinking that this will take days or weeks.
With the advent of technology and innovation, brute force attacks can happen in as fast as minutes. If you have a weak passcode, brute force attacks can easily hack into your system.
For example, using personal information like your birthday is a common guess most hackers will immediately make.
Keystroke Logging
There are different programs and malware out there that make use of keystroke logging. And how this works is it captures what you type on the keyboard.
Once malware sneaks into your computer, it can take note of the passwords you’ve been entering on your channels. Yikes!
Lost or Forgotten Passwords
Admittedly, I have a pretty bad memory. And honestly, one of the biggest struggles I face is trying to remember the different passwords I have for my different channels.
Just imagine, I have over five social media channels, and each of them consists of different alpha numerals.
And to remember my password, I’d often save them on the notes on my device. Worse, I write some of them on a piece of paper.
Sure enough, anyone who has access to the notes on my device or the piece of paper would know what my password is. And from there, I’m doomed.
They can sign in to my account just like that. Without any struggle or extra layer of protection.
But with two-factor authentication in place, there’s no chance for just anyone to access my account. They’ll need to validate the log-in through either a second device or notification only I have access to.
Phishing
Unfortunately, hackers are just as common as your standard robber on the streets. You can hardly tell who the hackers are, where they’re from, and how they’re able to get your information.
Hackers don’t make one big move. Instead, these are small calculated moves they make to test the waters.
I myself have been a victim of hacking, thanks to phishing attempts I wasn’t aware of back then.
Before, I used to receive these messages in my email that looked legitimate. It came from reputable companies, and there wasn’t anything unusual about it.
Without any red flags, I opened the link on the email, and everything went downhill from there.
Apparently, the links contain some malware, security tokens, or virus that can steal my password. How? Well, let’s just say that’s how advanced some hackers get.
And with knowledge of what my passwords are, they can pretty much sign in to my account. But again, factor authentication gives that extra layer of protection to make it impossible for hackers to get my information.
Different Two Factor Authentication Solutions to Protect Your Account
Like MFA, there are several 2FAs you can use to protect your account and confirm your identity.
I’ve listed down some of the most common types, which I enjoyed using. It gives me real-life updates, making sure no one gets access to my account except myself.
Push Authentication
Push authentication 2FA works just like how you’d get notifications on your device. It’s an extra layer of protection for your account, and you get a live update if there’s anything suspicious going on.
The beauty of push authentication is you get a detailed list of information about who’s trying to gain access to your account. This includes information like:
- Number of login attempts
- Time and location
- IP address
- Device used
And once you’ve received a notification about the suspicious behavior, you’ll be able to do something about it IMMEDIATELY.
SMS Authentication
SMS authentication is one of the most common types out there. Personally, it’s what I use most of the time, considering how I always have my mobile device with me.
Through this method, I receive a security code or OTP through text. I then enter the code on the platform, before I’m able to sign in.
The beauty of SMS authentication is they’re easy and simple to use. The whole process takes as fast as seconds, it’s hardly a hassle!
Also worth mentioning is that SMS authentication also works by texting you if there’s any suspicious activity with your account.
Today, SMS authentication is one of the most commonly accepted factor authentication methods. It’s so common that the majority of online platforms have this in place.
Enabling SMS authentication is standard practice, although you may choose not to enable it.
To Sum It All up About Two Factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA is one of the most common ways to keep your online data secure and protected. You can get live updates either by SMS or push notification.
Personally, the live updates I get from 2FA help me a lot. I can resolve any issues instantly!
Two-Factor Authentication & Multi-Factor Authentication: Is There a Difference?
The user experience is a critical consideration for any application or system, and ensuring a seamless and user-friendly experience is important for user adoption and satisfaction.
In addition, user identities must be protected to ensure the security of the system and prevent unauthorized access.
Identity verification processes, such as two-factor authentication, can help ensure that users are who they claim to be and prevent fraudulent access.
However, it’s important to balance security measures with the user experience, as overly cumbersome or complex authentication processes can frustrate users and hinder adoption.
Overall, ensuring a positive user experience while maintaining secure user identities is crucial for any system or application.
To put it simply, yes. There are some differences between (2FA) two-factor authentication and (MFA) multi-factor authentication.
Two-factor authentication/2FA, like its name suggests, makes use of two different ways to identify your identity. This could be a combination of your password & SMS notification, for example.
Multi-factor authentication/MFA, on the other hand, means the use of two or three different factors to identify your identity. It may be a combination of your password, SMS notification, and OTP.
At the end of the day, you set how you want to protect your account.
The two are generally interchangeable because two-factor authentication (2FA) is just another form of multifactor authentication (MFA).
Which is Better: MFA or 2FA?
Getting asked the question of which between multi-factor authentication solution/MFA or two-factor authentication solution/2FA works the best isn’t anything new to me.
I get that question all the time, and strangely enough, many users think there’s a right and wrong answer to this.
Having an extra two or more layers of protection and security is a big plus. But is it foolproof? Well, I’d like to give it the benefit of the doubt and say yes.
So is MFA better than 2FA?
In a word, yes. MFA sets the standard for high data protection especially for sensitive information like credit card details, accounting documents, finance reports, etc.
So far, factor authentication hasn’t proved me wrong. I haven’t been a victim of any phishing or cyberattacks ever since I’ve been extra careful now.
And we’re sure you’d want that for yourself too.
If I’m being honest, 2FA and MFA security solutions have their pros and cons, depending on the user.
It’s a matter of how many levels of protection and security you want for yourself. For me, two-factor authentication is sufficient.
But if I’m feeling extra cautious, I’d choose (MFA) multi-factor authentication as a security measure. Better safe than sorry right?
After all, imagine how difficult it would be for a hacker to hack through fingerprint authentication.
Questions & Answers
Wrap Up
Keeping your online data and information is vital, and I can’t emphasize enough how authentication factors in your safety and security. It’s crucial for users of today.
Regardless if you’re an individual or a small business organization, it pays to know there’s an extra layer of security you can employ for your online accounts.
Try out these authentication factors today. The best place to start is with your social media account. Instagram users can even already integrate 2FA to their account!
References
- https://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/definition/inherence-factor
- https://www.pcmag.com/encyclopedia/term/one-time-password
- https://www.kaspersky.com/resource-center/definitions/brute-force-attack
- https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/keystroke
- https://www.kaspersky.com/resource-center/definitions/what-is-an-ip-address
